An Analysis of Injury Severities in School Bus Accidents Based on Random Parameter Logit Models
-
摘要:
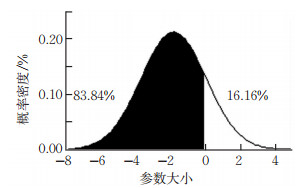
为深入分析安全因素对校车事故伤害严重程度的影响,探寻事故数据中未观察到的异质性,基于随机参数Logit模型从驾驶员、车辆、道路特征及环境4个方面构建校车事故伤害严重程度模型。结果表明:①涉事车辆数为2辆且对应参数服从正态分布时,不发生死亡受伤事故的概率为83.84%;②驾驶员年龄35~44岁、涉事车辆数为1辆时,死亡受伤事故概率均降低0.58%;③道路限速值为40~50 km/h时发生死亡受伤事故概率增加0.35%,道路限速值大于60 km/h时发生死亡受伤事故概率增加0.96%;④安全气囊状态打开,死亡受伤事故概率增加2.35%;⑤交通控制方式为车道标线时可能伤害事故概率增加1.85%,控制方式为中央分隔带时未受伤事故概率降低1.44%,死亡受伤事故发生概率却增加0.48%;⑥不安全时倒车转弯时发生可能伤害事故概率降低0.42%,分心驾驶、未按规定车道行驶、跟车太近和其他(饮酒)时未受伤事故概率分别增加1.36%,0.56%,0.39%和0.97%,可能受伤事故和死亡受伤事故发生概率却有所降低。
Abstract:This study develops an injury severity prediction model for the accidents involving school buses based on random parameter Logit model, in order to analyze the impacts of relevant factors on the injury severity of school bus accidents and the heterogeneity that is not observed in the accident data. The independent variables are from the following aspects: driver, vehicle, road characteristics and environment. It is found that: ①under the assumption that the corresponding parameters of the two involved vehicles follow the normal distribution, the probability of not having fatal and injury accidents of the school bus is 83.84%. ②The probability of a fatal injury is reduced by 0.58% when the driver is between 35 and 44 years old and the number of vehicles involved is one. ③When the road speed limit is between 40 and 50 km/h, the probability of injuries and fatal crashes increases by 0.35%;when the road speed limit is greater than 60 km/h, it increases by 0.96%. ④When the airbag is triggered, the probability of injuries and fatal crashes increases by 2.35%. ⑤When the traffic control mode is lane markings, the probability of possible injury accidents increases by 1.85%;when the control mode is the central divider, it decreases by 1.44%, while the probability of injuries and fatal crashes increases by 0.48%. ⑥The probability of possible injury accidents decreases by 0.42% when reversing turns under unsafe conditions; the probability of uninjured accidents increases by 1.36%, 0.56%, 0.39%, and 0.97%, respectively as distracted driving, missing lane driving, being too close to cars, and other factors(i.e. drinking), but the probability of accidents involving possible injury, and fatal crashes reduces.
-
Key words:
- traffic safety /
- school bus accident /
- injury severity /
- mixed Logit model /
- random parameters
-
表 1 影响因素定义及统计描述
Table 1. Definition and statistical description of influencing factors
序号 影响因素 变量符号 描述 频数(比例/%) 1 驾驶员性别 X1 男 1 209(50.04) — 女 1 207(49.96) 2 驾驶员年龄/岁 — < 25 221(9.15) X2 25~34 463(19.16) X3 35~44 427(17.67) X4 45~54 456(18.87) X5 55~64 514(21.27) X6 > 64 335(13.87) 3 安全带使用 X7 是 2 258(93.46) — 否 158(6.54) 4 安全气囊状态 X8 打开 191(7.91) — 未打开 2 225(92.09) 5 不安全驾驶行为 — 没有不当行为 390(16.14) X9 分心驾驶 416(17.22) X10 不按规定车道行驶 162(6.71) X11 不安全时倒车、转弯 190(7.86) X12 不安全车速 485(20.07) X13 未能让出道路优先权 192(7.95) X14 错误转弯 113(4.68) X15 跟车距离太近 78(3.22) X16 其他(饮酒等) 390(16.14) 6 涉事车辆数/辆 X17 1 439(18.17) X18 2 1 915(79.26) — 3 62(2.57) 7 道路限速值/(km/h) — 5~30 409(16.93) X19 30~40 1 019(42.18) X20 40~50 564(23.34) X21 50~60 192(7.95) X22 > 60 232(9.60) 8 是否在交叉口 X23 是 775(32.08) — 否 1 641(67.92) 9 光线条件 — 白天 2 105(87.13) X24 黄昏/黎明 1 12(4.64) X25 夜有灯 85(3.52) X26 夜无灯 114(4.72) 10 控制方式 — 无 706(29.22) X27 信号控制 421(17.43) X28 停车让行/指示牌 447(18.50) X29 车道标线 168(23.39) X30 中央分隔带 168(6.95) X31 其他 109(4.51) 11 是否在城区 — 是 1 698(70.28) X32 否 718(29.72) 12 是否在学校区域 — 是 71(2.94) X33 否 2 345(97.06) 注:“—”表示参考类别,不纳入模型进行拟合。 表 2 共线性诊断结果
Table 2. Results of co-linearity diagnostics
序号 变量 VIF 序号 变量 VIF 序号 变量 VIF 1 X17 7.67 12 X9 1.80 23 X32 1.29 2 X18 7.19 13 X27 1.78 24 X14 1.29 3 X5 2.83 14 X16 1.75 25 X26 1.24 4 X4 2.63 15 X29 1.75 26 X15 1.21 5 X2 2.58 16 X28 1.65 27 X31 1.16 6 X3 2.51 17 X21 1.60 28 X25 1.14 7 X6 2.36 18 X11 1.48 29 X8 1.11 8 X20 2.26 19 X13 1.46 30 X1 1.11 9 X19 2.16 20 X23 1.39 31 X33 1.05 10 X12 1.96 21 X10 1.36 32 X7 1.05 11 X22 1.87 22 X30 1.35 33 X24 1.04 表 3 校车事故伤害严重程度的随机参数Logit模型标定
Table 3. Calibration of the mixed Logit model for the severity of school bus accident injuries
变量 参数估计 t-Ratio 平均弹性系数(%) C B A A:死亡、严重伤害和非失能性伤害 驾驶员年龄:35~44岁 -0.897 -2.78 0.47 0.11 -0.58 道路限速: > 60 km/h 1.028 3.49 -0.77 -0.18 0.96 涉事车辆数:1辆 -1.594 -4.58 0.52 0.06 -0.58 涉事车辆数:2辆(均值) -1.859 -2.32 0.25 0.15 -0.39 涉事车辆数:2辆(标准差) 1.882 2.63 B:可能伤害 安全气囊状态:打开 2.335 4.49 -1.92 -0.43 2.35 控制方式:车道标线 0.568 4.01 -1.70 1.85 -0.15 C:未受伤 不安全驾驶行为:不安全时倒车转弯 -1.509 -3.81 0.39 -0.42 0.02 截距项 1.859 17.73 — — — 道路限速值:40~50 km/h -0.342 -2.66 -1.32 0.97 0.35 控制方式:中央分隔带 -1.016 -5.19 -1.44 0.96 0.48 不安全驾驶行为:分心驾驶 0.865 4.69 1.36 -0.95 -0.41 不安全驾驶行为:未按规定车道行驶 0.745 2.91 0.56 -0.41 -0.15 不安全驾驶行为:跟车太近 1.463 3.57 0.39 -0.28 -0.12 -
[1] NIRUPPAMA N, HAFEZI H. A short communication on school bus accidents: A review and analysis[J]. Natural Hazards, 2014, 74 (3): 2305-2310. doi: 10.1007/s11069-014-1255-8 [2] 陈昭明, 徐文远, 曲悠扬, 等. 基于混合Logit模型的高速公路交通事故严重程度分析[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2019, 37 (3): 42-50. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1674-4861.2019.03.006CHEN Zhaoming, XU Wenyuan, QU Youyang, et al. Analysis of highway traffic accident severity based on mixed Logit model[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2019, 37 (3): 42-50. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1674-4861.2019.03.006 [3] 何雅琴, 段雨阳, 王晨. 基于累积Logistic模型的行人交通事故严重程度分析及对策研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2021, 21 (3): 1165-1172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ202103036.htmHE Yaqin, DUAN Yuyang, WANG Chen. Analysis and countermeasures of pedestrian traffic accident severity based on cumulative Logistic model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2021, 21 (3): 1165-1172. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ202103036.htm [4] 宋栋栋, 杨小宝, 祖兴水, 等. 基于均值异质性随机参数Logit模型的城市道路事故驾驶员受伤严重程度研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2021, 21 (3): 214-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXT202103027.htmSONG Dongdong, YANG Xiaobao, ZU Xingshui, et al. Study on the severity of driver injury in urban road accidents based on mean heterogeneity random parameter Logit model[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021, 21 (3): 214-220. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXT202103027.htm [5] 王燕, 方景敏, 王霞. 安全视角下的校车运营与管理体系研究: 以济南市为例[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(社会科学版), 2014, 14 (1): 15-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQJS201401005.htmWANG Yan, FANG Jingmin, WANG Xia. Study on school bus operation and management system from the perspective of safety-taking Jinan city as an example[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University(Social Science Edition), 2014, 14(1): 15-18. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQJS201401005.htm [6] 陈涛, 王栋, 魏朗. 中美校车安全标准比较研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2012, 22 (5): 147-153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2012.05.023CHEN Tao, WANG Dong, WEI Lang. Comparative study on school bus safety standards in China and America[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2012, 22 (5): 147-153. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2012.05.023 [7] HU Xiaofeng, WU Jiansong, BAI Yiping, et al. Quantitative analysis of school safety events in China[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Resilience, 2020, 1 (2): 73-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jnlssr.2020.07.002 [8] WU Jiansong, FANG Weipeng, TONG Xing, et al. Bayesian analysis of school bus accidents: A case study of China[J]. Natural Hazards, 2019, 95 (3): 463-483. doi: 10.1007/s11069-018-3491-9 [9] LI Yanwu, SU Guofeng, ZHANG Xiaole, et al. Analysis of school bus accidents in China[J]. Natural Hazards, 2015, 79 (2): 723-734. doi: 10.1007/s11069-015-1867-7 [10] 潘立军, 刘喜梅. 校车安全事故故障树分析及安全运营对策研究[J]. 湖南社会科学, 2019 (4): 127-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLSH201904018.htmPAN Lijun, LIU Ximei. School bus safety accident fault tree analysis and safety operation countermeasures research[J]. Hunan Social Science, 2019 (4): 127-132. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLSH201904018.htm [11] 林庆丰, 邓院昌. 基于Logistic的城市公交事故严重程度影响因素分析: 以广东省为例[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 59 (4): 120-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSDZ202004014.htmLIN Qingfeng, DENG Yuanchang. Logistic analysis of influencing factors of urban bus accident severity: A case study of Guangdong province[J]. Journal of Sun Yat-sen University (Natural Science), 2020, 59 (4): 120-127. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSDZ202004014.htm [12] 胡骥, 闫章存, 卢小钊, 等. 基于有序Logit与Probit模型的交通事故严重性影响因素分析[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2018, 18 (3): 836-843. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201803004.htmHU Ji, YAN Zhangcun, LU Xiaozhao, et al. Analysis of factors influencing traffic accident severity based on ordered Logit and Probit model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2018, 18 (3): 836-843. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201803004.htm [13] CELIK A K, OKTAY E. A multinominal logit analysis of risk factors influencing road traffic injury severities in the Erzurum and Kars provinces of Turkey[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2014 (72): 66-77. [14] LIU Pengfei, FAN W D. Modeling head-on crash severity with drivers under the influence of alcohol or drugs(DUI) and non-DUI[J]. Traffic Injury Prevention, 2020, 21 (1): 7-12. doi: 10.1080/15389588.2019.1696964 [15] LIN Zijing, FAN W D. Cyclist injury severity analysis with mixed-logit models at intersections and nonintersection locations[J]. Journal of Transportation Safety and Security, 2021, 13(2): 223-245. doi: 10.1080/19439962.2019.1628140 [16] 汤左淦. 考虑异质性效应的翻车事故伤害严重程度模型对比研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019.TANG Zuogan. Comparative study on injury severity model of rollover accident considering heterogeneity effect[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2019. (in Chinese) [17] 马壮林, 邵春福, 李霞. 基于Logistic模型的公路隧道交通事故严重程度的影响因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40 (2): 423-426. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY201002024.htmMA Zhuanglin, SHAO Chun, LI Xia. Research on the influence factors of traffic accident severity in highway tunnel based on Logistic model[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2010, 40 (2): 423-426. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY201002024.htm [18] 史楠楠, 诸立超. 不同Halton抽样方法在随机参数Logit模型的比较[J]. 武汉理工大学学报(交通科学与工程版), 2016, 40 (5): 913-918. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.2095-3844.2016.05.030SHI Nannan, ZHU Lichao. Comparison of different Halton sampling methods in random parameter Logit model[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology(Transportation Science and Engineering), 2016, 40 (5): 913-918. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3963/j.issn.2095-3844.2016.05.030 [19] CERWICK D M, GKRITA K, SHAHEED M S, et al. A comparison of the mixed logit and latent class methods for crash severity analysis[J]. Analytic Methods in Accident Research, 2014, 3 (4): 11-27. [20] 张渤. 机动车与摩托车翻车事故受伤严重程度分析[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2018.ZHANG Bo. Injury severity analysis of vehicle and motorcycle rolover accident[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018. (in Chinese) [21] 侯芹忠. 考虑异质性与内生性的高速公路交通事故随机参数模型[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.HOU Qinzhong. Random parameters model for freeway traffic crash considering heterogeneity and endogeneity[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019. [22] WALLIS L A. Injuries associated with airbag deployment[J]. Emergency Medicine Journal, 2002, 19 (6): 490-493. doi: 10.1136/emj.19.6.490 [23] 葛如海, 陈珣, 张学荣, 等. 校车儿童安全气囊安全性仿真分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2015, 25 (3): 9-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK201503002.htmGE Ruhai, CHEN Xun, ZHANG Xuerong, et al. Safety simulation analysis of school bus children airbag[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2015, 25 (3): 9-15. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK201503002.htm [24] 蒋卫东. 道路中央分离带的安全性分析[J]. 公路交通技术, 2004, 4 (2): 78-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6477.2004.02.023JIANG Weidong. Safety analysis of road central separation belt[J]. Highway Traffic Technology, 2004, 4 (2): 78-80. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6477.2004.02.023 [25] 周志将, 袁黎, 崔二娟, 等. 城市道路中央分隔带设计对交通安全影响分析[J]. 公路工程, 2012, 37 (4): 69-72+108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGL201204015.htmZHOU Zhijiang, YUAN Li, CUI Erjuan, et al. Analysis on the impact of urban road central divider design on traffic safety[J]. Highway Engineering, 2012, 37 (4): 69-72+108. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGL201204015.htm [26] WU Qiong, ZHANG Guohui, CHEN Cong, et al. Heterogeneous impacts of gender-interpreted contributing factors on driver injury severities in single-vehicle rollover crashes[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2016, 94 (9): 28-34. [27] ANARKOOLI A J, HOSSEINPOUR M, KARDAR A. Investigation of factors affecting the injury severity of single-vehicle rollover crashes: A random-effects generalized ordered probit model[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2017, 106 (9): 399-410. [28] YU Bing, ZHANG Weigong, CAI Yingfeng. A lane departure warning system based on machine vision[C]. 2008 IEEE Pacific-Asia Workshop on Computational Intelligence and Industrial Application, Wuhan, China: IEEE, 2008. -





 下载:
下载: